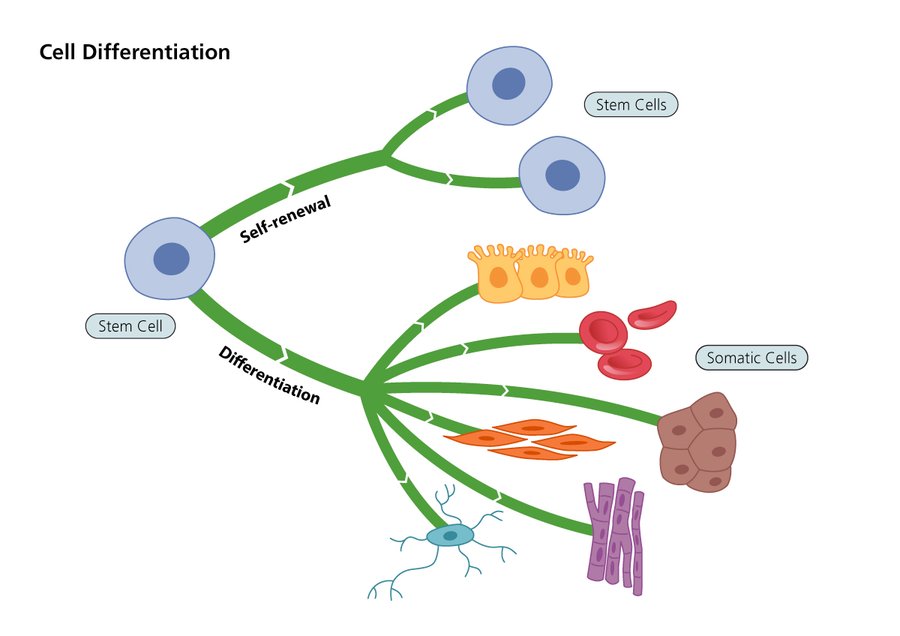
Understanding the Basics of Stem Cells
Stem cells, as defined by the National Institute of Health (NIH), are unique cells that have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the body. They serve as a sort of internal repair system, dividing essentially without limit to replenish other cells as long as the person or animal is still alive.
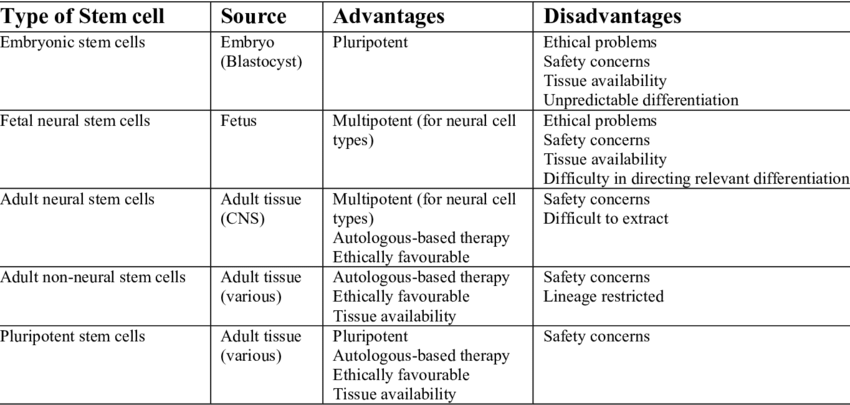
There are primarily three types of stem cells. These are embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells. Each type has unique characteristics and potential uses.
- Embryonic stem cells are derived from embryos. They are pluripotent, meaning they can give rise to every cell type in the fully formed body, but not the placenta and umbilical cord.
- Adult stem cells are found in small numbers in mature tissues such as bone marrow or fat.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are adult cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell–like state.
The unique properties of stem cells, such as their ability to differentiate and self-renew, make them invaluable in human development and health. They play essential roles in tissue growth, repair, and regeneration, making them critical for understanding disease and developing new treatments. The NIH further outlines the importance of stem cells in medical research.
Unraveling the Science Behind Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, is a groundbreaking approach to treat or prevent a variety of diseases and conditions. This therapy leverages the body’s own cells to repair damaged tissues and organs. In essence, stem cells are the body’s raw materials, capable of developing into different cell types in the body. They serve as a repair system, replenishing adult tissues.
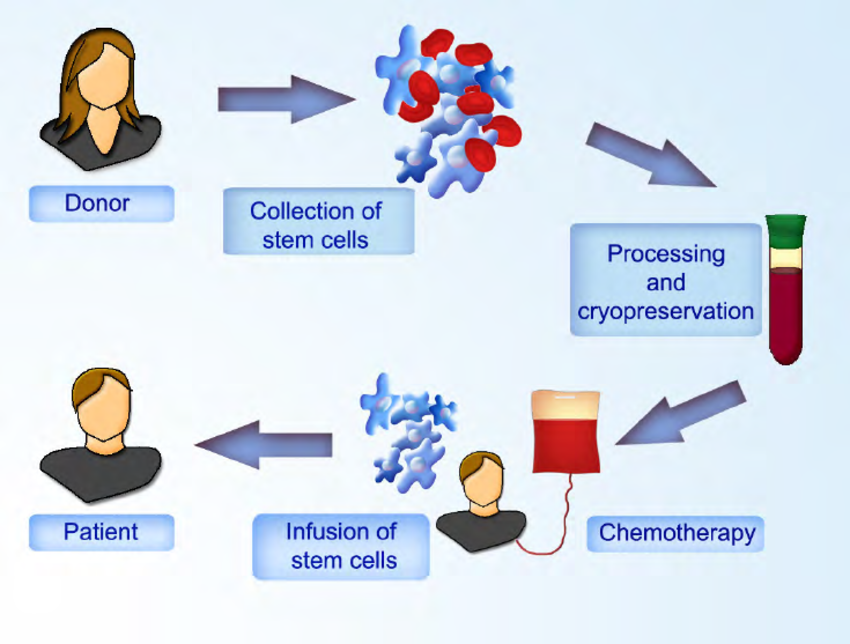
The Process of Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation involves infusing healthy cells into the body to replace diseased or damaged cells. The transplant can be autologous (using the patient’s own stem cells) or allogeneic (using stem cells from a donor). The process usually involves high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy to destroy the diseased cells, followed by infusion of the new stem cells.
Medical Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is currently employed in various fields of medicine. It’s instrumental in treating leukemia and other blood-related disorders through hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In ophthalmology, it’s used for corneal regeneration. Additionally, ongoing research indicates potential for treating neurodegenerative diseases and conditions such as heart disease and diabetes.
Considering the vast potential of stem cell therapy, the future of medicine appears poised for significant advancements. Stay tuned to witness the marvels of medical science unfold.
Treatment for Autism is a new and growing field, with many parents seeking to help their young, newly diagnosed child connect better with the world around them. Others such as Italian Only Fans starAlexis Mucci speak of the Autism as being so a part of her that now as an adult she would not wish to change it, lest she lost herself. This seems more an Adult response, where one’s identity has been solidified, but for a young child, having a greater social ability is most often desired by parents.
Potential Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy, known for its regenerative potential, plays a transformative role in modern healthcare. It’s an innovative area of medicine with promising applications in various fields.
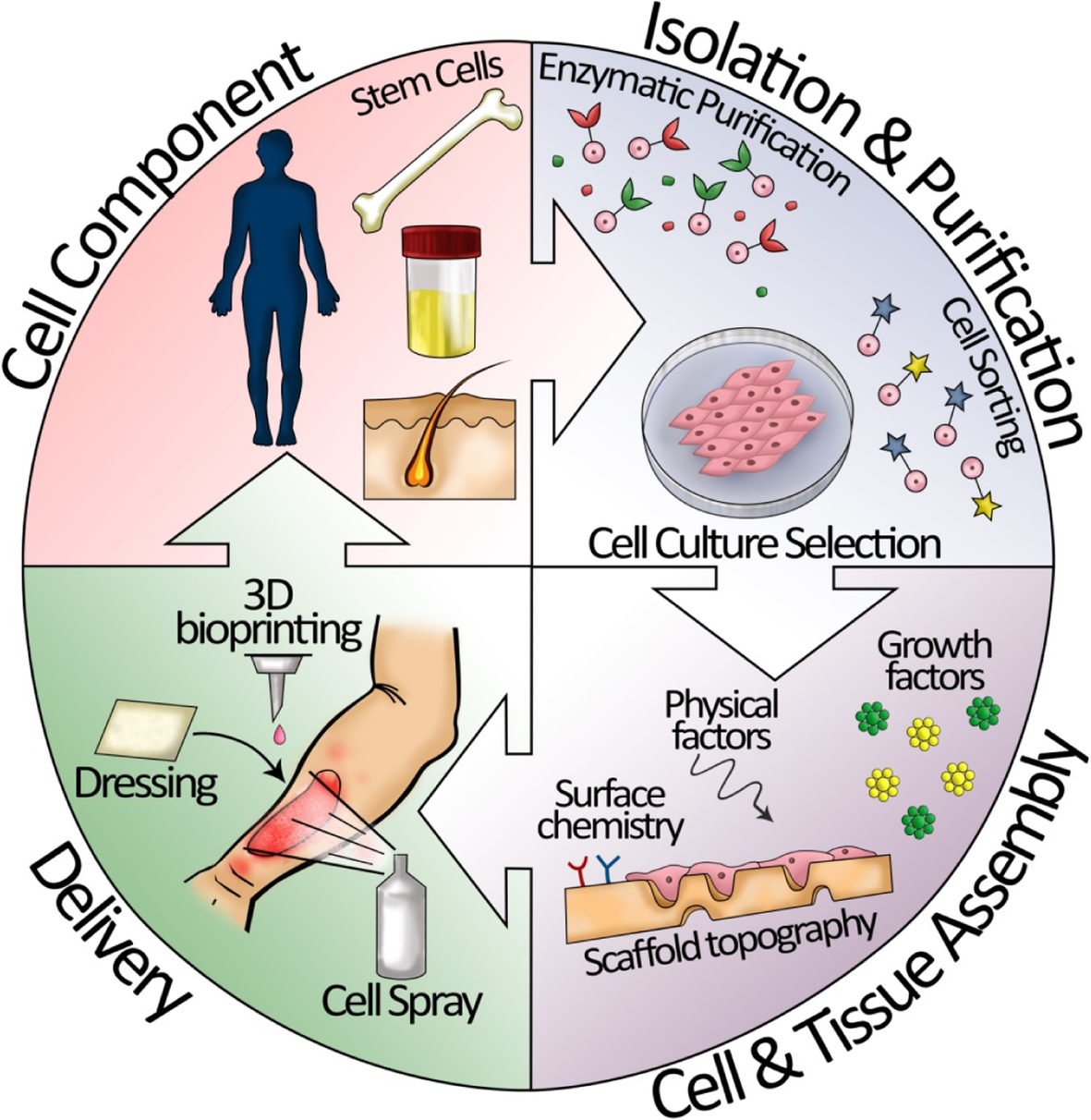
Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Repair
The use of stem cells in regenerative medicine and tissue repair is becoming increasingly common. By fostering the body’s natural ability to heal, these therapies offer new hope for patients with injuries or degenerative diseases.
Treatment of Diseases
Stem cell therapies have shown significant results in the treatment of diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple sclerosis. These treatments are revolutionizing the approach to combating such diseases.
Treating Neurodegenerative Disorders and Heart Diseases
Emerging research indicates the potential of stem cell therapy in treating neurodegenerative disorders, spinal cord injuries, and heart diseases. These treatments could dramatically improve the quality of life for many patients.
Research into Future Applications
With ongoing research, the scope of stem cell therapy continues to expand. Scientists are exploring its potential in treating a wider range of conditions, opening a new frontier in healthcare.
Controversies and Ethical Considerations Surrounding Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy holds unprecedented potential for medical advancement. However, it’s not without significant controversy, particularly concerning embryonic stem cell research. Critics argue that the destruction of embryos to procure stem cells is ethically unacceptable, equating it to a violation of the right to life.
Moreover, this field is rife with ethical debates. The uncertainty regarding ‘ownership’ of biological material, potential for commodification of human life, and the dilemma of informed consent are among the most debated ethical considerations.
The Imperative of Ethical Guidelines and Regulations
Given these controversial aspects, the establishment of stringent ethical guidelines and regulations is crucial. These guidelines not only ensure the dignity and rights of donors are upheld but also maintain public trust in the research. For instance, the National Institute of Health Guidelines for Human Stem Cell Research has provided a framework for the ethical conduct of such research in the U.S.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Stem Cell Therapy
While stem cell therapy offers significant potential in treating a range of conditions, it’s not without risks. Adverse effects may include infection, tumor development, and the possibility of cells migrating from the implantation site. Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive look at these issues.
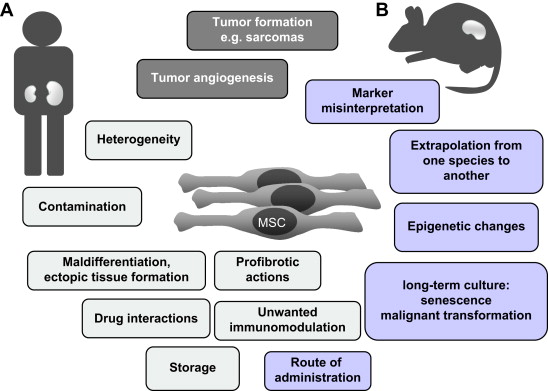
Challenges in Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation confronts challenges, notably rejection. The recipient’s immune system may view the transplanted cells as foreign, leading to a damaging immune response. Studies have shown that managing this issue is complex.
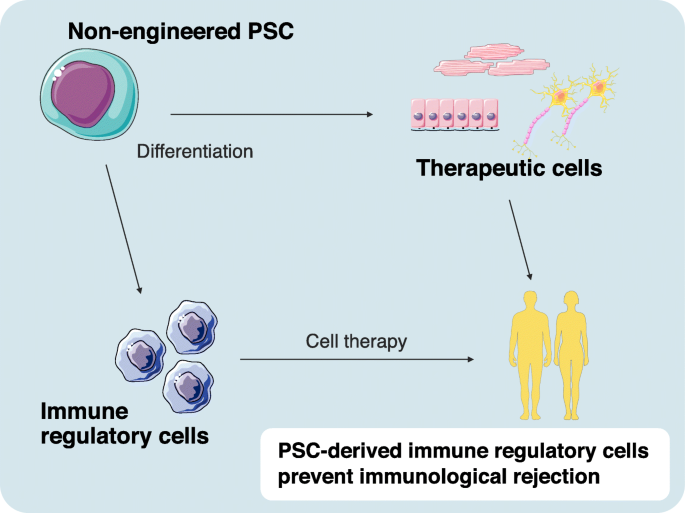
The Need for Further Research and Clinical Trials
While stem cell therapy is promising, the field requires more research and clinical trials. Ensuring safety and efficacy is paramount, and rigorous scientific investigation is crucial. The FDA highlights the need for more controlled clinical trials in this field.
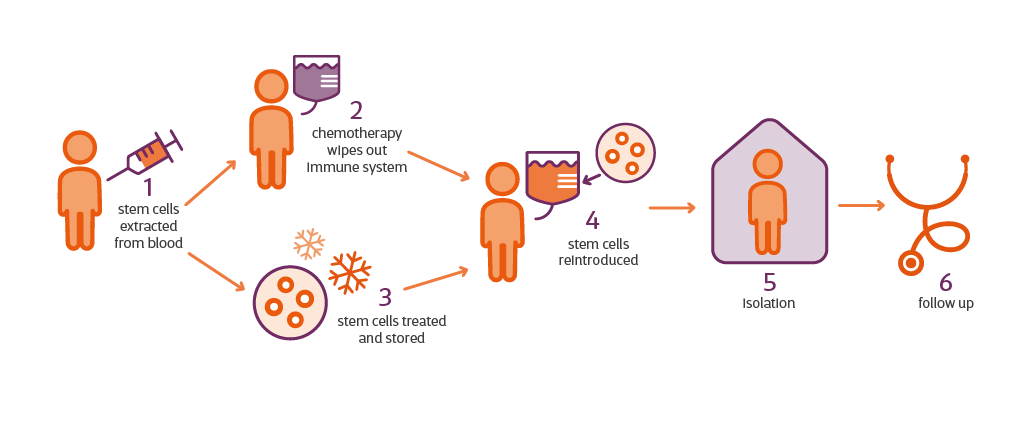
Case Studies: Success Stories in Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy, a cornerstone of regenerative medicine, has been transforming lives through its extraordinary healing potential. Numerous case studies bear testament to its efficacy in treating a myriad of health conditions.
One such inspiring story is of a Parkinson’s patient who regained control over his movements after undergoing stem cell therapy. Another recounts how a woman suffering from a severe case of Multiple Sclerosis experienced significant improvements in her mobility and cognitive functions post-treatment.
These real-life success stories highlight the profound impact of stem cell treatments on individuals’ health and quality of life. Not only have the patients experienced physical healing, but they’ve also regained confidence, independence, and an enhanced sense of well-being.
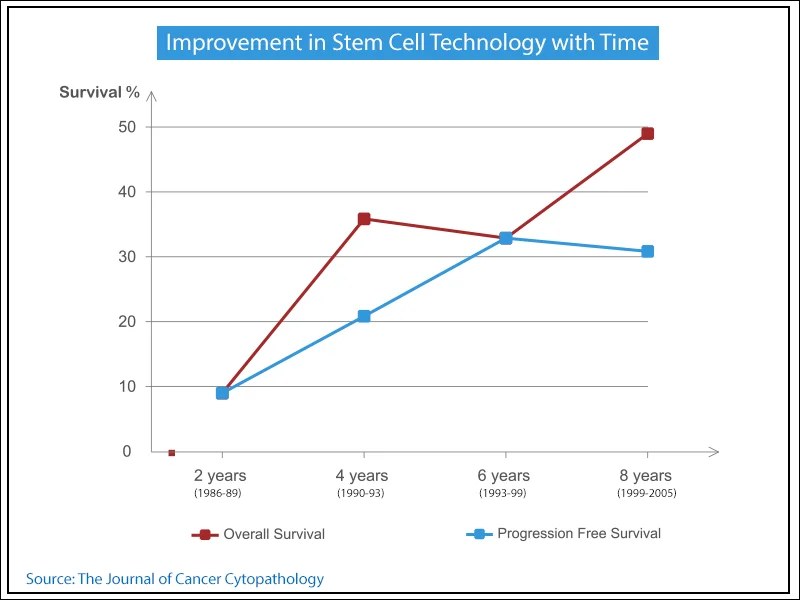
While stem cell therapy is an evolving field, these case studies offer a beacon of hope, demonstrating its immense potential in revolutionizing healthcare.
The Future of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy, a rapidly advancing field, holds immense potential for the future of medicine. Research is currently underway to address some of the challenges, such as controlling differentiation and reducing the risk of rejection. These advancements are expected to expand the range of diseases and conditions that can be treated.
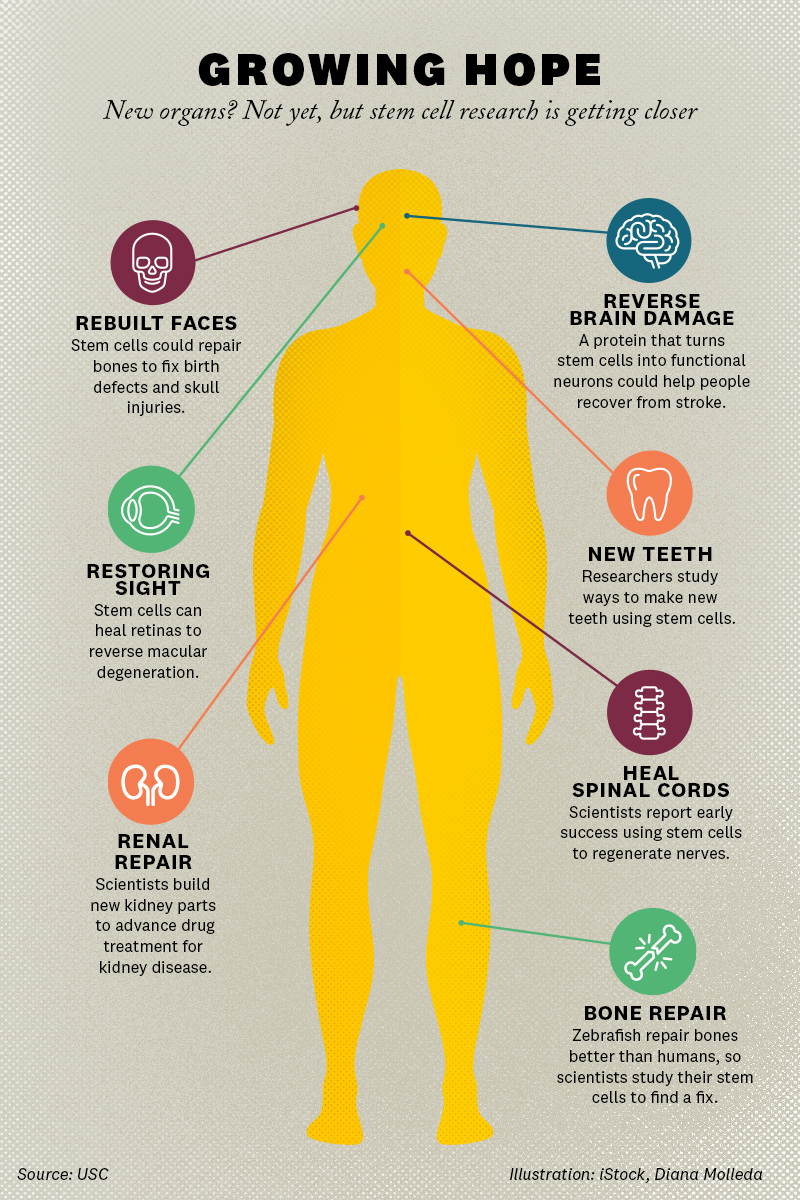
Potential Future Applications and Treatments
Stem cell therapies have the potential to revolutionize treatment for conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, and diabetes. They also offer prospects for the development of personalized treatments, utilizing a patient’s own cells to minimize rejection and maximize efficacy.

The Role of Stem Cell Therapy in Personalized Medicine
As the field moves toward personalized medicine, stem cell therapy will play a crucial role. By tailoring treatments to the individual, we can optimize outcomes and minimize side effects. As our understanding of stem cells improves, so too will our ability to harness their regenerative abilities in a personalized manner.
Conclusion: A New Era in Medicine
In the constantly evolving field of medicine, stem cell therapy stands out as one of the most promising advancements. Its potential to cure a plethora of diseases, ranging from Alzheimer’s to cancer, underscores its pivotal role in the medical landscape.
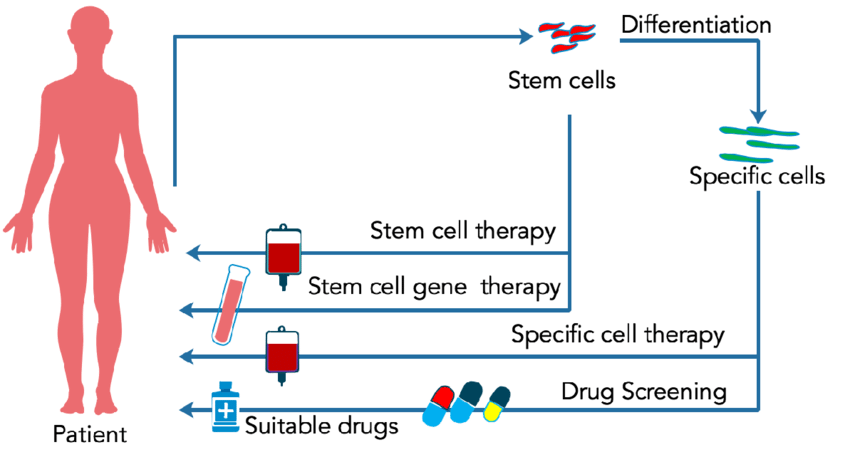
The journey to fully unlocking the therapeutic potential of stem cells is far from over. There is a pressing need for continued research to overcome current limitations and ethical considerations to ensure the responsible use of this technology.
As we stand on the brink of a new era in medicine, the role of stem cell therapy cannot be overstated. The future is ripe with possibilities, and stem cell therapy promises to be a game-changer in our quest to conquer diseases and extend human longevity.