Table of Contents
Stem Cells and Diabetes: A New Horizon in Treatment
Stem cells, the building blocks of life, are unique cells that possess the ability to develop into various cell types in the body. They offer significant potential for regenerating damaged tissues and organs, opening new doors in the treatment of numerous diseases.
Among these diseases is diabetes, a chronic condition that impacts the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to a host of health complications. Diabetes affects millions of Americans, putting a strain on their daily lives and overall health.
Currently, diabetes is managed with insulin injections, oral medications, and lifestyle changes. However, these treatments do not cure the disease, but only control its symptoms. This article will explore the groundbreaking potential of stem cells as a treatment for diabetes. By delving into this innovative approach, readers can expect to gain an understanding of how stem cells could revolutionize diabetes treatment, offering a potential cure rather than just symptom management.
Understanding Stem Cells: Unleashing the Power of Regeneration
At the heart of every organism’s ability to grow and repair lies a microscopic marvel – the stem cell. These are cells with the unique ability to develop into many different types of cells in the body, serving as a sort of internal repair system.
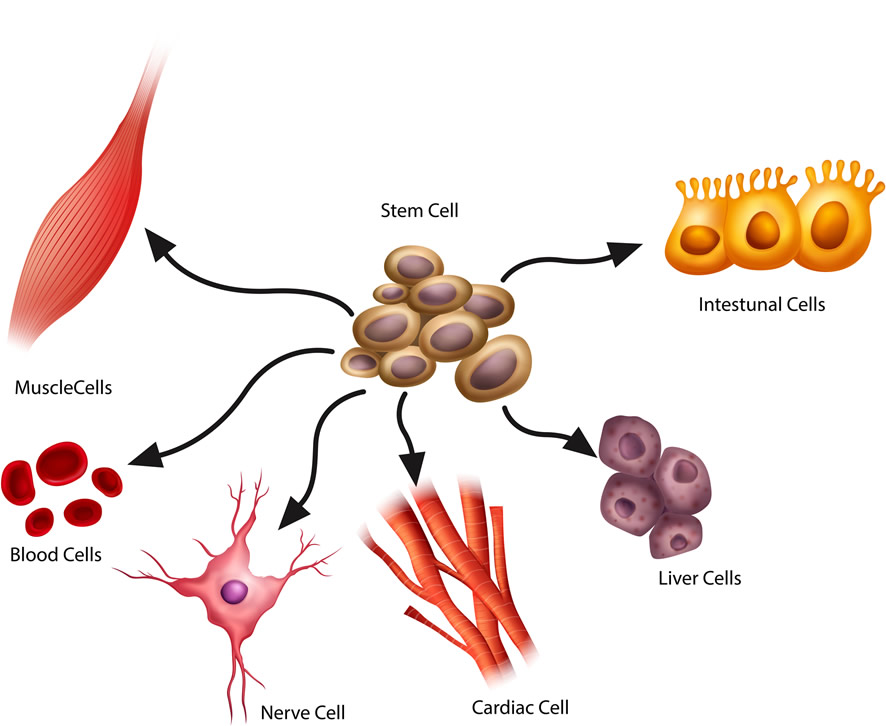
Types of Stem Cells
There are several types of stem cells, but two are most commonly used in research: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells come from unused embryos from fertility treatments, while adult stem cells are found in small numbers in most adult tissues, such as bone marrow or fat.
Stem Cell Differentiation
Stem cells differentiate into specialized cells through a process called cell differentiation. This transformation from unspecialized to specialized function is guided by the cell’s DNA, which carries specific instructions for all the structures and functions a cell will have.
Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine
In the field of regenerative medicine, stem cells are seen as a valuable resource due to their ability to regenerate damaged tissues. Researchers are exploring the potential for stem cells to be used in treatments for a variety of diseases, including diabetes, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s. Their unique properties offer potential for healing and hope for patients worldwide.
Stem Cells: A Potential Game-Changer in Diabetes Treatment
Diabetes, a chronic disease characterized by high levels of blood sugar, is currently managed through diet, exercise, and insulin therapy. However, the advent of stem cell research is reshaping the landscape of potential treatment options.
How Stem Cells Can Treat Diabetes
Stem cells are unique in that they can develop into many different cell types. In the context of diabetes, scientists are particularly interested in their potential to produce insulin-producing beta cells. In theory, these new beta cells could replace those destroyed by the patient’s immune system in type 1 diabetes, or rejuvenate malfunctioning ones in type 2 diabetes.
Potential Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy could provide a more definitive solution to diabetes. By addressing the root cause of the disease — the loss or malfunctioning of beta cells — stem cell therapy could potentially eliminate the need for insulin injections and significantly improve the quality of life for patients.
Stem Cell Therapy vs. Traditional Treatment Methods
Traditional treatment methods manage symptoms but do not cure the disease. Stem cell therapy, on the other hand, offers the potential for a cure. While still in the experimental stages, early results from clinical trials show promise, and may revolutionize diabetes treatment in the future.
Types of Stem Cells Utilized in Diabetes Treatment
Stem cell research has opened new horizons in diabetes treatment, with several types of stem cells being investigated for their potential therapeutic value. These include embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells.
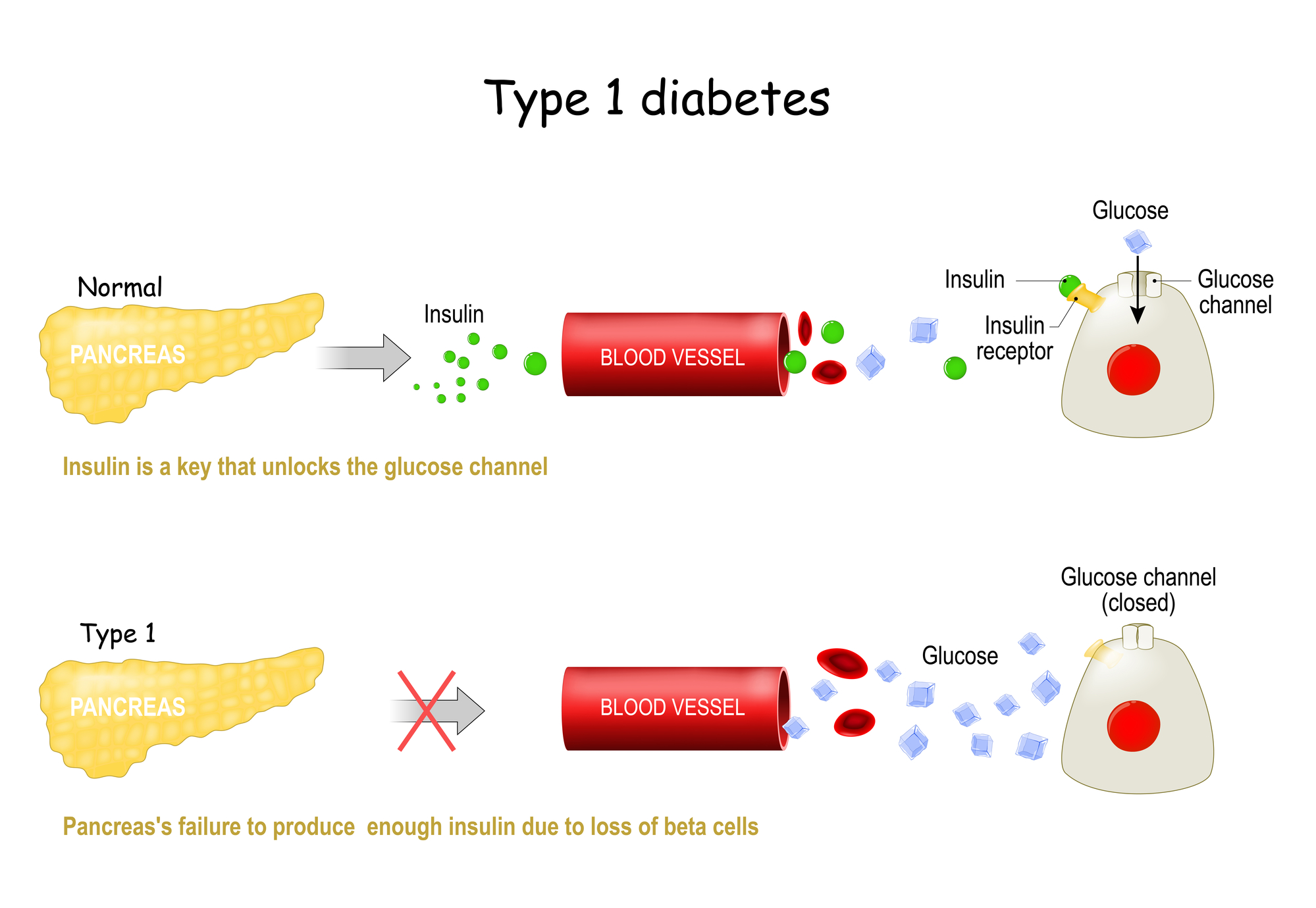
Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) have the remarkable ability to differentiate into any cell type, including insulin-producing beta cells. However, ethical considerations and the risk of immune rejection pose challenges to its application.
Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells, specifically mesenchymal stem cells, have also shown promise. They are usually harvested from the patient’s own body, reducing the risk of immune rejection. However, their differentiating potential is lower compared to ESCs.Studies have shown that these cells can be induced to become insulin-producing cells.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are adult cells genetically reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell–like state, potentially overcoming the ethical and immune rejection issues associated with ESCs. iPSCs have the potential to differentiate into insulin-secreting cells, paving the way for patient-specific diabetes treatment.
Comparing Stem Cells for Diabetes Treatment
While each type of stem cell offers unique advantages, their suitability for diabetes treatment varies. ESCs and iPSCs have broad differentiating potential but face ethical and safety concerns, while adult stem cells pose fewer ethical issues but have limited differentiating potential.
Understanding the Stem Cell Transplantation Process
Stem cell transplantation, a promising therapeutic approach for diabetes, involves the collection and transplantation of stem cells into the patient. The process is composed of several crucial stages.
Collection of Stem Cells
The first step is the collection of stem cells, typically harvested from the bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood of the patient or a suitable donor. This is conducted under sterile conditions to prevent contamination.
Isolation and Purification of Stem Cells
Following collection, the stem cells are isolated and purified using specialized techniques. This ensures the collected cells are indeed stem cells and free from any possible contaminants. Quality control measures are strictly enforced at this stage.
Methods of Stem Cell Transplantation
Once purified, stem cells can be transplanted back into the patient. This can be achieved through intravenous infusion or direct injection into the site needing repair. The goal is to prompt these cells to develop into insulin-producing cells, addressing the root cause of diabetes.
Challenges and Risks Associated with Stem Cell Transplantation
Despite its potential, stem cell transplantation is not without challenges and risks. These include possible infection, rejection of the transplanted cells, and the risk of cancer due to the uncontrolled growth of transplanted cells. Research is ongoing to mitigate these risks, making stem cell transplantation a safer treatment option for diabetes. Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive overview of these challenges.
Success Stories and Clinical Trials: Stem Cell Therapy in Treating Diabetes
Stem cell therapy holds immense potential in the field of medicine, particularly for conditions like diabetes. Over the years, there have been several notable success stories where this treatment has shown promising results.
Success Cases in Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes
One of the biggest breakthroughs in the field was a study published in 2020, where researchers successfully introduced insulin-producing cells into a patient with Type 1 diabetes. These cells were derived from human embryonic stem cells, marking a significant milestone in using stem cell therapy for diabetes treatment.
Ongoing Clinical Trials and Outcomes
Several clinical trials are currently underway to further explore the effectiveness of stem cell therapy in treating diabetes. For example, the University of Miami’s Diabetes Research Institute is conducting a trial to determine whether stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood can help regenerate insulin-producing cells in patients with Type 1 diabetes.
Potential Future Developments
As researchers continue to delve into the potential of stem cell therapy, the future for diabetes treatment looks promising. The ultimate goal is the development of a universal cure for diabetes, using stem cells to regenerate the body’s ability to produce insulin. This would represent a monumental leap forward in not only treating but potentially eradicating diabetes.

Ethical Considerations, Controversies, and Public Perception in Stem Cell Therapy
The use of embryonic stem cells in research and therapy has raised ethical concerns due to the methods of obtaining these cells. Embryonic stem cells often come from discarded embryos following in vitro fertilization, a process which some find controversial, as they believe the embryo has moral and legal status equal to a human being.
However, stem cell therapy presents significant potential for treating chronic diseases, such as diabetes. Unfortunately, the public perception of stem cell therapy is often clouded by misconceptions and misinformation. Many are unaware of the differences between embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells, the latter of which can be harvested from the individual requiring treatment, thus bypassing the ethical concerns associated with embryonic cells.
Regulation and guidelines for stem cell research and treatment are essential to ensure ethical practices. In the U.S., the National Institutes of Health (NIH) provides guidelines governing stem cell research, establishing the framework for ethical and responsible practices.
With proper understanding and regulation, stem cell therapy could revolutionize the treatment of diabetes, offering a solution to restore the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. However, public acceptance and understanding of this treatment method are vital for its further development and application.
Limitations and Challenges of Stem Cell Therapies for Diabetes
Current stem cell therapies for diabetes, while offering promising potential, are not without their limitations. The primary challenge lies in the difficulty of controlling the differentiation of stem cells into insulin-producing cells, an essential requirement for the effective treatment of diabetes. This complexity makes it challenging to develop consistent, effective treatments.
Potential Side Effects and Complications
Stem cell therapy is not without potential side effects and complications. These can range from minor issues like infection at the injection site to more serious problems such as the development of tumors. Additionally, ethical issues arise from the use of embryonic stem cells, adding another layer of complexity to this form of treatment.(source)
Conclusion: The Future of Stem Cell Therapy in Diabetes Treatment
Stem cell therapy emerges as a potential game-changer in the treatment of diabetes, showing remarkable promise in restoring insulin production and reversing the disease’s effects. The research conducted to date reveals the incredible potential of this innovative approach.
Call to Action: Further Research and Development
While these findings are encouraging, it is crucial to continue research and development in this field. Further exploration and scientific trials can help us fully understand the benefits and limitations of stem cell therapy in diabetes treatment.
Exploring Stem Cell Therapy as a Treatment Option
For individuals with diabetes, exploring stem cell therapy as a potential treatment option could be life-changing. Stay informed about the latest developments and discuss with your healthcare provider the possibility of incorporating stem cell therapy into your treatment plan.
