Introduction to Stem Cells and Their Role in Neurology
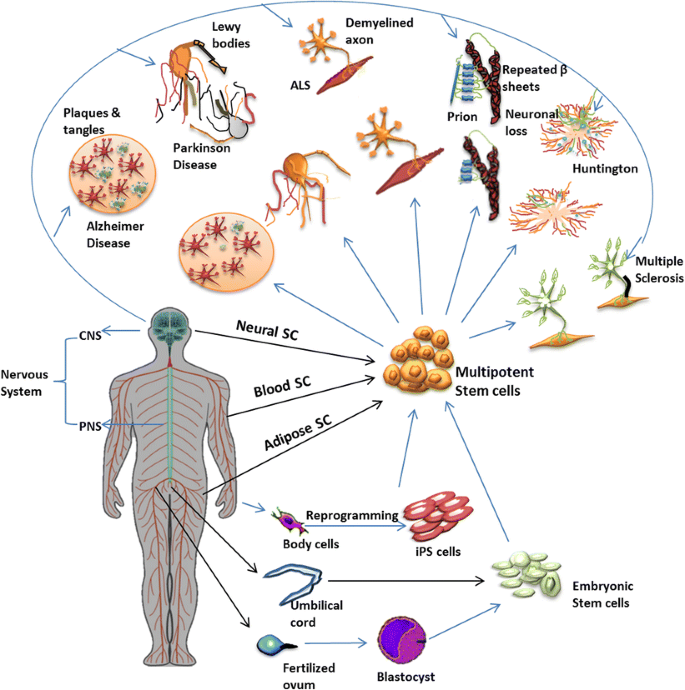
Stem cells, often referred to as the body’s ‘master cells,’ have the unique ability to develop into virtually any type of cell in the human body. These self-renewing and multi-potent cells play a crucial role in repair, regeneration, and maintenance of our body’s tissues and organs.

When it comes to neurology, stem cells hold immense promise. They can potentially be used to replace or repair damaged cells in the brain, offering new hope for treating neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. This regenerative capability is central to the field of neurorestoratology, which explores the potential use of stem cells to restore neurological function.
As we continue to delve into the complexities of stem cells and their applications in neurology, we are uncovering the potential for groundbreaking treatments that could change the future of medicine.
Current Application of Stem Cells in Neurology
The rapidly evolving field of neurology is experiencing a paradigm shift with the application of stem cell treatments. These therapies aim to provide a revolutionary approach to treating debilitating neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Multiple Sclerosis. Recent studies have demonstrated positive results in using pluripotent stem cells to replace damaged neurons and restore neurological function.
Case Studies and Success Stories of Stem Cell Treatments in Neurological Conditions
Several case studies have shown promising results in using stem cells to treat neurological disorders. For example, in a groundbreaking study, patients with multiple sclerosis showed significant improvement after stem cell transplantation.

Limitations and Challenges of Current Stem Cell Treatments
Despite the potential, stem cell therapies are not without limitations and challenges. The primary concerns include the ethical implications of stem cell research, the potential for tumorigenicity, and the technical difficulties in ensuring the survival and integration of transplanted stem cells into the patient’s existing neural network.
Latest Advances in Stem Cell Research for Neurological Conditions
Neurology has experienced remarkable discoveries in stem cell research. Scientists are now able to use stem cells to reproduce disease-specific neurons, providing unprecedented opportunities for disease modeling and drug screening. This advancement could overcome the current limitations in neurological treatments.
One of the most promising findings is the use of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These cells, derived from the patient’s own body, can be reprogrammed into any cell type, including neurons. This breakthrough spells hope for conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
The Future of Stem Cell Treatment in Neurology
These advances in stem cell research are reshaping the future of neurological treatment. The potential of stem cells to restore neuronal function could mark the advent of curative therapies for neurological conditions that were previously considered untreatable.
Although still in experimental stages, the development of brain organoids from stem cells is another promising area of research. These mini-brains provide an accurate model for studying disease progression and testing potential therapies.

The continued exploration of stem cells in neurology promises a future where the management and treatment of neurological disorders will be revolutionized.
Potential Future Applications of Stem Cell Therapy in Neurology
Emerging research in the field of neurology signals a promising future for stem cell therapies. These innovative treatments could revolutionize how we manage neurological disorders.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Conditions like Parkinson’s Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, and ALS may be treated using stem cells to replace damaged neurons and support the regeneration of brain tissues.
- Spinal Cord Injuries: Stem cells could facilitate the healing of spinal cord injuries by regenerating lost nerve cells and reconnecting broken neural pathways.
- Stroke Recovery: Stem cell therapy has the potential to quicken stroke recovery by promoting the repair of damaged brain tissue.
The theoretical benefits of these future treatments are immense. They could improve patient outcomes and redefine neurological care as we know it.
Despite the remarkable potential, stem cell therapies are still experimental, and their long-term effects are yet to be fully understood. Therefore, ongoing research and clinical trials are vital to ensure their safety and efficacy.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations in Stem Cell Research
Stem cell research, particularly embryonic stem cell research, is a hotbed of ethical debate. Concerns primarily pertain to the moral implications of creating, using, and destroying embryos. The National Institute of Health has established guidelines to address these ethical issues, advocating for the use of excess in vitro fertilization (IVF) embryos. These embryos would otherwise be discarded.
Current Regulations on Stem Cell Use
Currently, the FDA allows using stem cells in treatment under certain conditions, primarily for blood disorders. However, many other potential uses are still under investigation and are not approved for clinical use.
Future Regulatory Changes
The dynamic nature of stem cell research suggests that we can anticipate regulatory changes in the future. As science progresses and the potential for new treatments becomes clearer, the FDA is expected to adapt its regulations to accommodate these advancements while ensuring patient safety.
Challenges and Limitations of Stem Cell Therapy in Neurology
Despite its enormous potential, stem cell therapy in neurology faces several technical and scientific hurdles. A major challenge is the delivery of stem cells into the brain. The blood-brain barrier prevents many substances from reaching the brain, making it difficult to ensure effective treatment.
Furthermore, the specific targeting of stem cells remains a significant challenge. A precise cell delivery system is needed to ensure that the stem cells reach the desired location in the brain.
Limitations of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy also has its limitations when it comes to treating neurological conditions. For instance, it may not be effective in treating chronic neurological diseases due to the irreversible damage to neural cells.
Solutions to Overcome These Challenges
One promising solution to these challenges is the use of bioengineered materials to enhance the survival and integration of transplanted stem cells into the host tissue. Additionally, advancements in gene editing technologies could potentially improve the specificity of stem cell targeting.
Economic Impact of Stem Cell Treatments in Neurology
The cost implications of stem cell treatments for neurological conditions are substantial. These avant-garde treatments often entail high upfront costs, creating a significant financial burden for patients and healthcare systems. Research indicates that the average cost of stem cell therapies can range from several thousand to over $100,000, depending on the condition and treatment complexity.

However, successful stem cell therapies can bring about long-term economic benefits. For instance, these therapies can result in substantial cost savings by potentially reducing the need for ongoing treatments and hospitalizations. Furthermore, as these treatments continue to evolve and become more mainstream, economies of scale may help reduce costs.
Impact on Healthcare Systems and Insurance
Current healthcare systems and insurance models are grappling with how to cover these treatments. The high cost and uncertainty surrounding their efficacy pose challenges. Nonetheless, studies suggest that the long-term economic impact could be positive by decreasing the overall burden of chronic neurological conditions.
With the rapid advances in stem cell treatments, it’s vital that we continue to evaluate and adapt our economic models to ensure that these potentially life-changing treatments are accessible to those who need them most.
Conclusion: The Uncharted Potential of Stem Cell Treatments in Neurology
Stem cell treatments have immense potential in neurology. From neurodegenerative diseases to traumatic brain injuries, these therapies hint at a groundbreaking shift in medical science.
Imagine a world where Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, or spinal cord injuries are not lifelong sentences but curable conditions. This is not science fiction; it’s the very real promise of stem cell research in neurology.
The Future of Stem Cell Treatments in Neurology
The future of stem cell treatments in neurology is not just promising; it’s imperative. The demand for effective neurological treatments will only rise with an aging global population. Yet, the journey is only beginning. The complexity of the human brain and the ethical considerations surrounding stem cell research pose significant challenges.
A Call to Action for Further Research and Investment
It’s clear that we need to invest more in this area – more research, trials, and funding. This isn’t just about pushing the boundaries of medical science; it’s about improving the quality of life for millions of people around the world. So, let’s invest in the potential of stem cells in neurology. Our future depends on it.
